Zimbabwe’s Disease Surveillance recorded 344 new cases of mumps in the week ending 12 May 2024, which took the cumulative number of infections to 4,486, according to the Ministry of Health and Child Care.
Of the new cases, Mashonaland Central, Mashonaland West and Mashonaland East had the highest number of cases with 92, 67 and 52 respectively. This factsheet provides key facts about mumps.
What is Mumps?
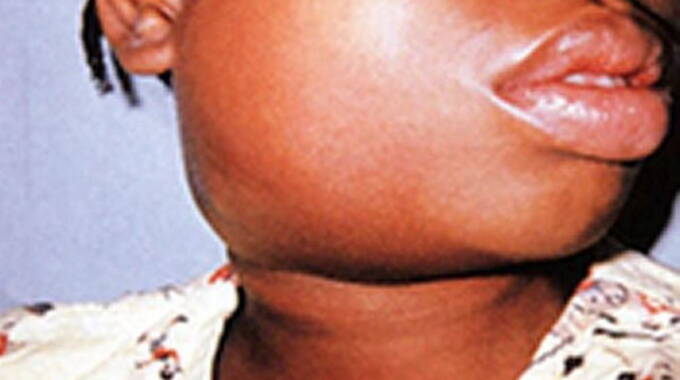
Mumps is an acute viral illness caused by a virus called paramyxovirus, which causes inflammation of the parotid salivary glands – a condition known medically as Parotitis.
In the pre-vaccine era, mumps was primarily a childhood disease which affected adults in very rare instances.
What are the signs and symptoms of mumps
- Mumps is primarily a respiratory infection frequently accompanied by viremia (virus in the blood stream) which targets the salivary glands.
- The most common and characteristic clinical presentation of mumps is an acute and tender parotid swelling which develops 16–18 days after exposure in up to 70% of cases.
- Mumps may present as a lower respiratory tract infection, particularly in young children.
How are mumps transmitted?
Mumps are spread from person to person through direct contact with saliva or respiratory droplets of a person infected with the virus.
Mumps typically requires close contact to spread, especially among vaccinated populations. Close contact is defined as:
- having direct contact with a mumps patient’s infectious respiratory secretions by droplet transmission (e.g., kissing, sharing saliva-contaminated objects like water bottles, or being coughed or sneezed on).
- being in close proximity for a prolonged period of time with a person infected with mumps during their infectious period (2 days prior, to 5 days after, onset of parotitis or other salivary gland swelling)
What prevention method works for mumps?
Immunisation is the only effective method of prevention.
Sources
Ministry of Health and Child Care
European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control
Centre for Disease Control
Related content
Do you want to use our content? Click Here